[ad_1]
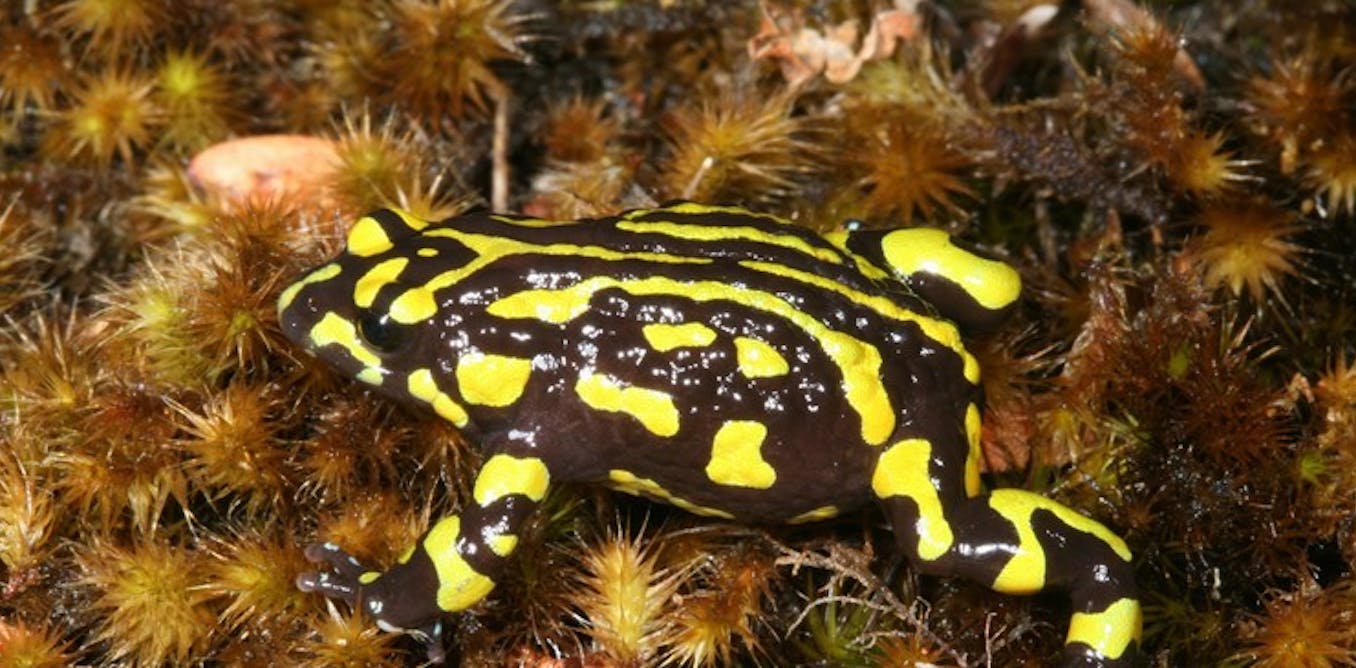
Within the late Nineteen Seventies in southeast Queensland, a silent killer arrived on Australian shores. The victims had been our distinctive frogs, with the primary to fall being the exceptional gastric brooding frog, final seen in 1981.
Greater than three a long time on, we all know that the killer was a illness referred to as chytridiomycosis, attributable to amphibian chytrid fungus.
This fungus is answerable for the presumed extinction of an extra 5 Queensland frog species, and the decline and disappearances of many native populations throughout Australia’s whole east coast and tablelands, together with species that had been as soon as widespread and customary. Globally, a whole lot of amphibian species have additionally suffered main declines or at the moment are thought of to be extinct on account of this illness.
Picture Lee Berger
In a examine printed in Wildlife Analysis, we and our colleagues determine seven extra Australian frogs which can be at rapid threat of extinction by the hands of chytrid fungus, together with the long-lasting Corroboree frogs (each southern and northern species), Baw Baw frog, noticed tree frog, Kroombit tinker frog, armoured mist frog and the Tasmanian tree frog. We predict that the following few years could present the final probability to save lots of these species.
Whereas the six already extinct Queensland species all declined quickly after the arrival of chytrid, declines in southern areas have been slower. Chytrid is but to reach in areas of Tasmania’s Wilderness World Heritage Space, though the implications are more likely to be simply as extreme.
Our work aimed to prioritise frog conservation efforts throughout Australia, figuring out the species most liable to chytrid, and subsequently most in want of pressing motion. Worryingly, we discovered that 5 of the seven high-risk species that we recognized lack a sustained and adequately funded monitoring program to guard them.
Along with the seven species at rapid threat of extinction, we recognized an extra 22 which can be at average to low threat. We additionally assessed the adequacy of present conservation efforts for all of those species, and located that almost all restoration efforts depend on the goodwill of people and are poorly resourced.
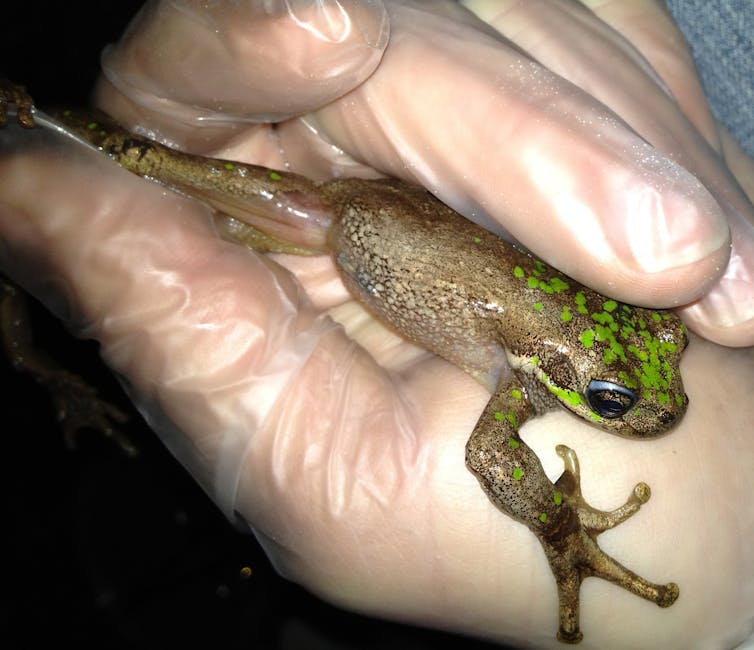

A wholesome Tasmanian tree frog.
It’s doable to handle the menace posed by chytrid fungus, however fast motion is urgently wanted. We now have recognized six vital administration actions which can be required to forestall additional extinctions of Australian frogs and name for an impartial administration and analysis fund to deal with the approaching menace.
The seven species at excessive threat require proactive restoration applications. Crucial administration actions could embrace: broad-scale surveys; intensive monitoring; exact threat evaluation; the event of husbandry strategies for the institution of assurance colonies; re-introductions and or translocations; and new administration methods to keep up wild populations.
Australia initially led the world in efforts to determine and handle chytrid fungus, which was listed as a “key threatening course of” by state and federal governments in 2002
In 2006, a plan was drawn up to fight the illness, delivering extra analysis funding and leading to drastically improved biosecurity measures and elevated understanding of the fungus.
In 2012 the plan was reviewed, and a revised plan that includes current analysis developments now awaits approval. However motion is required to handle the impression of the fungus, and disappointingly there was no funding allotted to implement the brand new plan.
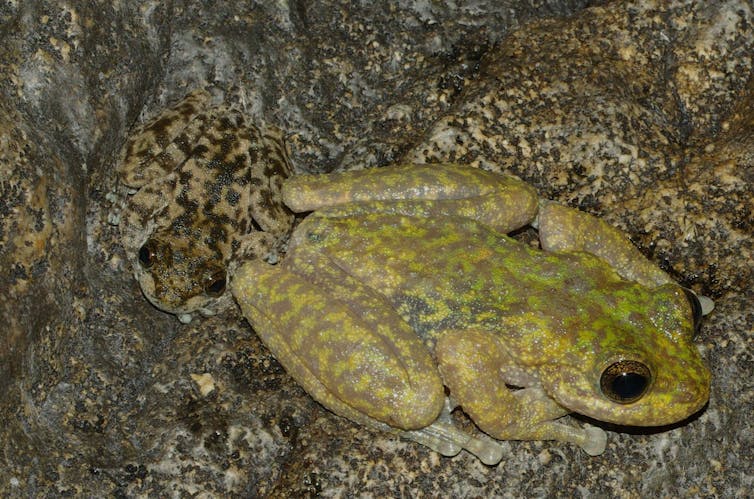

Blink and also you’ll miss them: the armoured mist frog (left) and waterfall frog.
The previous decade has additionally seen main cuts in each state and federal authorities assets for wildlife conservation. State companies have disbanded devoted restoration groups and there was a shift away from single species conservation measures in an effort to maximise restricted funding. That is regardless of the obligations set out in laws to preserve particular person threatened species. These cuts have severely undermined frog conservation efforts.
These frogs shouldn’t be allowed to go the identical manner because the Christmas Island pipistrelle, which might arguably have been saved if the federal authorities had heeded scientists’ warnings.
On a constructive observe, administration interventions have saved the critically endangered Southern Corroboree Frog from extinction for now, however it stays threatened by chytrid fungus and requires ongoing administration and analysis. With out swift motion, authorities help and the devoted efforts of many people, this species would undoubtedly already be gone.
[ad_2]
